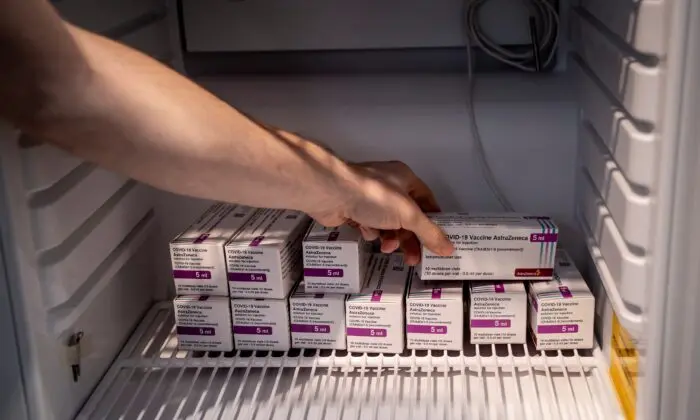
Inadequate storage could have resulted in many vaccine recipients receiving inert COVID-19 shots.
More than 20 percent of healthcare providers failed to comply with COVID-19 vaccine storage and monitoring requirements set by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which could have led to some of the administered vaccines becoming inert.
The study, published in the Vaccine journal on Dec. 27, looked at how healthcare providers taking part in the CDC’s COVID-19 vaccination program complied with the agency’s standards between May 2021 and May 2023. The study found that the overall compliance rate of all providers was only 63.3 percent.
While vaccine preparation, administration, and error reporting stages scored above 90 percent, vaccine storage and monitoring performed the worst among all stages, with a compliance rate of only 79.9 percent.
The study tracked 14 healthcare provider types, including public health providers, commercial vaccination service providers, state or local corrections/detention, health centers, home health, hospitals, IHS or tribal, long-term care, medical practice, pharmacy-chain, pharmacy-independent, and urgent care.
Vaccine storage and monitoring had a compliance rate lower than 80 percent among 11 out of 14 healthcare providers.
The lowest was among state or local corrections/detention at just 64 percent, followed by urgent care at 66.2 percent, and pharmacy-independent at 69.7 percent. The rest had a compliance rate of between 70 and 80 percent.
The low rates of vaccine storage and monitoring compliance is a key metric given that the two most used COVID-19 vaccines in the United States—Pfizer and Moderna—had strict temperature storage requirements.
Pfizer vaccines have to be stored in an ultra-cold freezer between -80 to -60 degrees Celsius, while Moderna vaccines must be frozen between -25 and -15 degrees Celsius.
Pfizer and Moderna vaccines have to be stored at low temperatures because they are mRNA vaccines. If not stored at low temperatures, the vaccines can break down and become useless.
An inert vaccine means the shot was inactive and lacked any chemical or biological action.
Experts from the CDC authored the Vaccine journal study. The authors stated they received no financial support from any organization for the work and that no other relationships or activities could have influenced the submitted study.
Vaccine Distribution Compliance
The Dec. 27 study observed that healthcare provider compliance was “high” when it came to COVID-19 vaccine preparation, administration, and error reporting categories. However, compliance was “lowest” for vaccine storage, handling, and reporting requirements.
The “reporting” category—which included immunization registry reporting, inventory reporting, temperature excursion, and vaccine wastage reporting—had a low compliance rate of 82.6 percent.
State or local corrections/detention had the lowest overall compliance rate of 45.7 percent, followed by urgent care at 46.9 percent.
The study pointed out that “of the 1,472 (8.6 percent) site visits reporting a temperature excursion within the past 30 days, 39.1 percent were non-compliant with CDC-required temperature excursion processes (e.g., quarantining impacted vaccine, storing vaccine in a backup unit, reporting the temperature excursion to the immunization program, and contacting the vaccine manufacturer for usability documentation).”
Temperature excursion refers to a situation wherein a pharmaceutical product is exposed to temperatures that are outside its prescribed range for storage and transportation.
The study insisted that “most healthcare providers that received a COVID-19 Vaccination Provider Oversight program site visit were compliant with program requirements overall and by compliance area.”
However, it admitted that “further research can strengthen vaccine storage, handling, and administration practices for future widespread vaccination efforts.”
Lessons learned from the CDC vaccine compliance program “will be important for future vaccine response activities and for building a broader U.S. Government routine vaccine program for adults,” the researchers wrote.
Studies have shown that many COVID-19 vaccines that were supposed to be administered to people ended up getting wasted.
According to a July 11, 2022, post by disease forecasting company Airfinity, an estimated 1.1 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines were wasted since the global rollout.
“Despite countries best efforts to avoid wastage, some degree is inevitable. Large multi-dose vials can make efficiencies more challenging, as well as cold chain storage and predicting daily demand or simply a vial being dropped or left out too long,” said Airfinity Analytics Director Dr. Matt Linley.
In June last year, the CDC revealed to NBC News that an estimated 82.1 million COVID-19 vaccine doses were wasted across the country between December 2020 and May 2022.
Retail pharmacies Walmart and CVS were found to be responsible for more than 25 percent of the wasted doses.
Make sure to SHARE this article on Facebook with your best friends!